Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2021;36:637-46, Yun-Ui Bae et al.)
- Ji Hong You, Yun-Ui Bae, Ho Chan Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1149-1150. Published online September 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.502
- [Original]
- 2,668 View
- 76 Download

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
- Yun-Ui Bae, Ji Hong You, Nan Hee Cho, Leah Eunjung Kim, Hye Min Shim, Jae-Hyung Park, Ho Chan Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):637-646. Published online June 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.962

- 5,174 View
- 147 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a progressive metabolic disease. Early detection of prediabetes is important to reduce the risk of T2DM. Some cytokines are known to be associated with T2DM. Therefore, we aimed to identify cytokines as novel biomarkers of glucose dysmetabolism.
Methods
The first stage of the study included 43 subjects (13 subjects with newly diagnosed T2DM, 13 with prediabetes, and 16 with normoglycemia) for cytokine microarray analysis. Blood samples of the subjects were assessed for 310 cytokines to identify potential indicators of prediabetes. The second stage included 142 subjects (36 subjects with T2DM, 35 with prediabetes, and 71 with normoglycemia) to validate the potential cytokines associated with prediabetes.
Results
We identified 41 cytokines that differed by 1.5-fold or more in at least one out of the three comparisons (normoglycemia vs. prediabetes, normoglycemia vs. T2DM, and prediabetes vs. T2DM) among 310 cytokines. Finally, we selected protein Z (PROZ) and validated this finding to determine its association with prediabetes. Plasma PROZ levels were found to be decreased in patients with prediabetes (1,490.32±367.19 pg/mL) and T2DM (1,583.34±465.43 pg/mL) compared to those in subjects with normoglycemia (1,864.07±450.83 pg/mL) (P<0.001). There were significantly negative correlations between PROZ and fasting plasma glucose (P=0.001) and hemoglobin A1c (P=0.010).
Conclusion
PROZ levels were associated with prediabetes and T2DM. We suggest that PROZ may be a promising biomarker for the early detection of prediabetes. Further large-scale studies are needed to evaluate the relationship and mechanism between PROZ and prediabetes and T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- On the human health benefits of microalgal phytohormones: An explorative in silico analysis
Angelo Del Mondo, Annamaria Vinaccia, Luigi Pistelli, Christophe Brunet, Clementina Sansone
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 1092. CrossRef - Role of F-box WD Repeat Domain Containing 7 in Type 1 Diabetes
Sarah W. Mohammed, Zainab M. Qassam, Ekhlass M. Taha, Nameer M. Salih
Ibn AL-Haitham Journal For Pure and Applied Sciences.2023; 36(3): 167. CrossRef - Identification of Protein Z as a Potential Novel Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Prediabetes
Seung-Hoi Koo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 572. CrossRef - Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2021;36:637-46, Yun-Ui Bae et al.)
Ji Hong You, Yun-Ui Bae, Ho Chan Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1149. CrossRef - Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2021;36:637-46, Yun-Ui Bae et al.)
Tiffany Pascreau, Maia Tchikviladze, Emilie Jolly, Sara Zia-Chahabi, Bertrand Lapergue, Marc Vasse
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1147. CrossRef
- On the human health benefits of microalgal phytohormones: An explorative in silico analysis

- Clinical Study
- Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
- Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):901-908. Published online December 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.787
- 6,850 View
- 232 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate clinical outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) positive patients with type 2 diabetes compared to those without diabetes in Korea.
Methods
We extracted claims data for patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea from January 20, 2020 to March 31, 2020. We followed up this cohort until death from COVID-19 or discharge from hospital.
Results
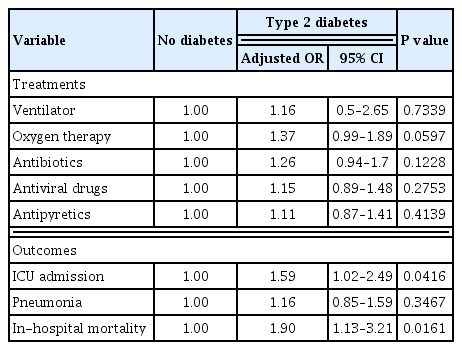
A total of 5,473 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 were analyzed, including 495 with type 2 diabetes and 4,978 without diabetes. Patients with type 2 diabetes were more likely to be treated in the intensive care unit (ICU) (P<0.0001). The incidence of inhospital mortality was higher in patients with type 2 diabetes (P<0.0001). After adjustment for age, sex, insurance status, and comorbidities, odds of ICU admission (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 1.59; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02 to 2.49; P=0.0416) and in-hospital mortality (adjusted OR, 1.90; 95% CI, 1.13 to 3.21; P=0.0161) among patients with COVID-19 infection were significantly higher in those with type 2 diabetes. However, there was no significant difference between patients with and without type 2 diabetes in ventilator, oxygen therapy, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antipyretics, and the incidence of pneumonia after adjustment.
Conclusion
COVID-19 positive patients with type 2 diabetes had poorer clinical outcomes with higher risk of ICU admission and in-hospital mortality than those without diabetes. Therefore, medical providers need to consider this more serious clinical course when planning and delivering care to type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19 infection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024; 48(1): 53. CrossRef - Predictors of COVID-19 outcome in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based study
Amira M. Elsayed, Mohamad S. Elsayed, Ahmed E. Mansour, Ahmed W. Mahedy, Eman M. Araby, Maha H. Morsy, Rasha O. Abd Elmoniem
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Pneumococcal Pneumonia
Catia Cilloniz, Antoni Torres
Diagnostics.2024; 14(8): 859. CrossRef - Risk for Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after COVID-19 among Korean Adults: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study
Jong Han Choi, Kyoung Min Kim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 245. CrossRef - The Intersection of COVID-19 and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview of the Current Evidence
Mykhailo Buchynskyi, Iryna Kamyshna, Valentyn Oksenych, Nataliia Zavidniuk, Aleksandr Kamyshnyi
Viruses.2023; 15(5): 1072. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - Diabetes and deaths of COVID-19 patients: Systematic review of meta-analyses
Aakriti Garg, Mahesh Kumar Posa, Anoop Kumar
Health Sciences Review.2023; 7: 100099. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and COVID-19 Outcomes in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis and Meta-regression of 84,011 Patients
Ru Ying Fong, Annie Lee, Fei Gao, Jonathan Jiunn Liang Yap, Khung Keong Yeo
Journal of Asian Pacific Society of Cardiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
A. V. Alieva, A. A. Djalilov, F. A. Khaydarova, A. V. Alimov, D. Z. Khalilova, V. A. Talenova, N. U. Alimova, M. D. Aripova, A. S. Sadikova
Obesity and metabolism.2023; 20(2): 92. CrossRef - Genetic Predictors of Comorbid Course of COVID-19 and MAFLD: A Comprehensive Analysis
Mykhailo Buchynskyi, Valentyn Oksenych, Iryna Kamyshna, Sandor G. Vari, Aleksandr Kamyshnyi
Viruses.2023; 15(8): 1724. CrossRef - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels predict outcome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Sylvia Mink, Christoph H. Saely, Andreas Leiherer, Matthias Frick, Thomas Plattner, Heinz Drexel, Peter Fraunberger
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Two years of SARS-CoV-2 infection (2019–2021): structural biology, vaccination, and current global situation
Waqar Ahmad, Khadija Shabbiri
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline haemoglobin A1c and the risk of COVID‐19 hospitalization among patients with diabetes in the INSIGHT Clinical Research Network
Jea Young Min, Nicholas Williams, Will Simmons, Samprit Banerjee, Fei Wang, Yongkang Zhang, April B. Reese, Alvin I. Mushlin, James H. Flory
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Incidence and Outcomes of COVID-19 Needing Hospital Admission According to Sex: Retrospective Cohort Study Using Hospital Discharge Data in Spain, Year 2020
Jose M. de Miguel-Yanes, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Javier de Miguel-Diez, Valentin Hernández-Barrera, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Ricardo Omaña-Palanco, Ana Lopez-de-Andres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2654. CrossRef - The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(9): 525. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, US-PIMA Indian, and Trinidadian Screening Scores for Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prediction
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2022; 10(21): 4027. CrossRef - New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus Presenting As Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients With COVID-19: A Case Series
Aysha Sarwani, Mahmood Al Saeed, Husain Taha, Rawdha M Al Fardan
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The management of type 2 diabetes before, during and after Covid-19 infection: what is the evidence?
Leszek Czupryniak, Dror Dicker, Roger Lehmann, Martin Prázný, Guntram Schernthaner
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19

- Diabetes
- Response: Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:275–81, Ji Hong You et al.)
- Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):424-425. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.424
- [Original]
- 3,265 View
- 45 Download

- Clinical Study
- Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song, Se Hee Park, Kyoung Hye Park, Joo Young Nam, Dong Wook Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):275-281. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.275
- 7,277 View
- 97 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Hyperglycemic crisis is a metabolic emergency associated with diabetes mellitus. However, accurate epidemiologic information on cases of hyperglycemic crisis in Korea remains scarce. We evaluated trends in hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations and in- and out-of-hospital mortality in Korea. We also predicted future trends.
Methods We extracted claims data with hyperglycemic crisis as the principal diagnosis from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea from January 2004 to December 2013. We investigated the numbers of claims with hyperglycemic crisis and identified trends in hyperglycemic crisis based on those claims data. We predicted future trends by statistical estimation.
Results The total annual number of claims of hyperglycemic crisis increased from 2,674 in 2004 to 5,540 in 2013. Statistical analysis revealed an increasing trend in hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations (
P for trend <0.01). In contrast, the hospitalization rate per 1,000 diabetes cases showed a decreasing trend (P for trend <0.01) during this period. The mortality rate per 1,000 diabetes cases also showed a decreasing trend (P for trend <0.0001). However, no distinct linear trend in the case-related fatality rate at <60 days over the last decade was observed. The predicted number of annual claims of hyperglycemic crisis will increase by 2030.Conclusion The number of hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations in Korea increased in the last decade, although the hospitalization rate per 1,000 diabetes cases and mortality rate decreased. Also, the predicted number of annual claims will increase in the future. Thus, it is necessary to establish long-term healthcare policies to prevent hyperglycemic crisis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing outcome prediction by applying the 2019 WHO DM classification to adults with hyperglycemic crises: a single-center cohort in Thailand
Chatchon Kaewkrasaesin, Weerapat Kositanurit, Phawinpon Chotwanvirat, Nitchakarn Laichuthai
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; : 103012. CrossRef - Obesity and 30-day case fatality after hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations in Korea: a national cohort study
Hojun Yoon, Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Sun Ok Song, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(3): 74. CrossRef - Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality
Mohammed K. Ali, Jonathan Pearson-Stuttard, Elizabeth Selvin, Edward W. Gregg
Diabetologia.2022; 65(1): 3. CrossRef - Comparison of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of pediatric patients with and without diabetic ketoacidosis at the time of type 1 diabetes diagnosis
Young-Jun Seo, Chang Dae Kum, Jung Gi Rho, Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(2): 126. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and outcomes of care in patients hospitalized with diabetic ketoacidosis
Mohsen S. Eledrisi, Haifaa Alkabbani, Malk Aboawon, Aya Ali, Imad Alabdulrazzak, Maab Elhaj, Ashraf Ahmed, Hazim Alqahwachi, Joanne Daghfal, Salem A. Beshyah, Rayaz A. Malik
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 192: 110041. CrossRef - Hyperglycemic Crisis Characteristics and Outcome of Care in Adult Patients without and with a History of Diabetes in Tigrai, Ethiopia: Comparative Study
Getachew Gebremedhin, Fikre Enqueselassie, Helen Yifter, Negussie Deyessa
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 547. CrossRef - Increased Incidence of Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis After COVID-19: A Two-Center Retrospective Study in Korea
Min Jeong Han, Jun Ho Heo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 783. CrossRef - Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 349. CrossRef - Letter: Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:275–81, Ji Hong You et al.)
Jang Won Son
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 422. CrossRef - Response: Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:275–81, Ji Hong You et al.)
Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 424. CrossRef
- Enhancing outcome prediction by applying the 2019 WHO DM classification to adults with hyperglycemic crises: a single-center cohort in Thailand

- Clinical Study
- Calpain-10 and Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Ji Sun Nam, Jung Woo Han, Sang Bae Lee, Ji Hong You, Min Jin Kim, Shinae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):364-371. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.364
- 3,529 View
- 50 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Genetic variations in calpain-10 and adiponectin gene are known to influence insulin secretion and resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Recently, several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in calpain-10 and adiponectin gene have been reported to be associated with type 2 diabetes and various metabolic derangements. We investigated the associations between specific calpain-10 and adiponectin gene polymorphisms and Korean type 2 diabetes patients.
Methods Overall, 249 type 2 diabetes patients and 131 non-diabetic control subjects were enrolled in this study. All the subjects were genotyped for SNP-43 and -63 of calpain-10 gene and G276T and T45G frequencies of the adiponectin gene. The clinical characteristics and measure of glucose metabolism were compared within these genotypes.
Results Among calpain-10 polymorphisms, SNP-63 T/T were more frequent in diabetes patients, and single SNP-63 increases the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. However, SNP-43 in calpain-10 and T45G and intron G276T in adiponectin gene were not significantly associated with diabetes, insulin resistance, nor insulin secretion.
Conclusion Variations in calpain-10, SNP-63 seems to increase the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in Koreans while SNP-43 and adiponectin SNP-45, -276 are not associated with impaired glucose metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decoding type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk variants in Pakistani Pashtun ethnic population using the nascent whole exome sequencing and MassARRAY genotyping: A case-control association study
Asif Jan, Zakiullah, Sajid Ali, Basir Muhammad, Amina Arshad, Yasar Shah, Haji Bahadur, Hamayun Khan, Fazli Khuda, Rani Akbar, Kiran Ijaz, Giuseppe Novelli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0281070. CrossRef - Silencing LncRNA PVT1 Reverses High Glucose-Induced Regulation of the
High Expression of PVT1 in HRMECs by Targeting miR-128-3p
Xuyang Wang, Wangling Chen, Wei Lao, Yunxin Chen
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(02): 119. CrossRef - Association of CAPN10 (SNP-19) genetic polymorphism and obesity with T2DM: a study on Bengali Hindu caste population
Pranabesh Sarkar, Diptendu Chatterjee, Arup Ratan Bandyopadhyay
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(1): 37. CrossRef - Association of Candidate Gene Polymorphism with Metabolic Syndrome among Mongolian Subjects: A Case-Control Study
Ariunbold Chuluun-Erdene, Orgil Sengeragchaa, Tsend-Ayush Altangerel, Purevjal Sanjmyatav, Batnaran Dagdan, Solongo Battulga, Lundiamaa Enkhbat, Nyamjav Byambasuren, Munkhzol Malchinkhuu, Munkhtstetseg Janlav
Medical Sciences.2020; 8(3): 38. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of the association between adiponectin SNP 45, SNP 276, and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yuwei Dong, Gongping Huang, Xin Wang, Zhaoming Chu, Jingzhi Miao, Houwen Zhou, Mingqing Xu
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(10): e0241078. CrossRef - Association of three SNPs in adiponectin gene with lipid traits of Tianzhu Black Muscovy (Cairina moschata)
Yuan-Yu Qin, Yi-Yu Zhang, Hua-Lun Luo, Lei Wu
Molecular Biology Reports.2019; 46(1): 325. CrossRef
- Decoding type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk variants in Pakistani Pashtun ethnic population using the nascent whole exome sequencing and MassARRAY genotyping: A case-control association study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



